XLMTM genetic cause and inheritance
XLMTM is a genetic disease
X-linked myotubular myopathy (XLMTM) is caused by mutations in the MTM1 gene, which encodes myotubularin, a protein required for the normal development, organization, and function of skeletal muscle cells.1-3 Approximately 400 unique mutations in the MTM1 gene have been associated with XLMTM in patients.4
The MTM1 gene is located on the X chromosome, and XLMTM is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner.1,2
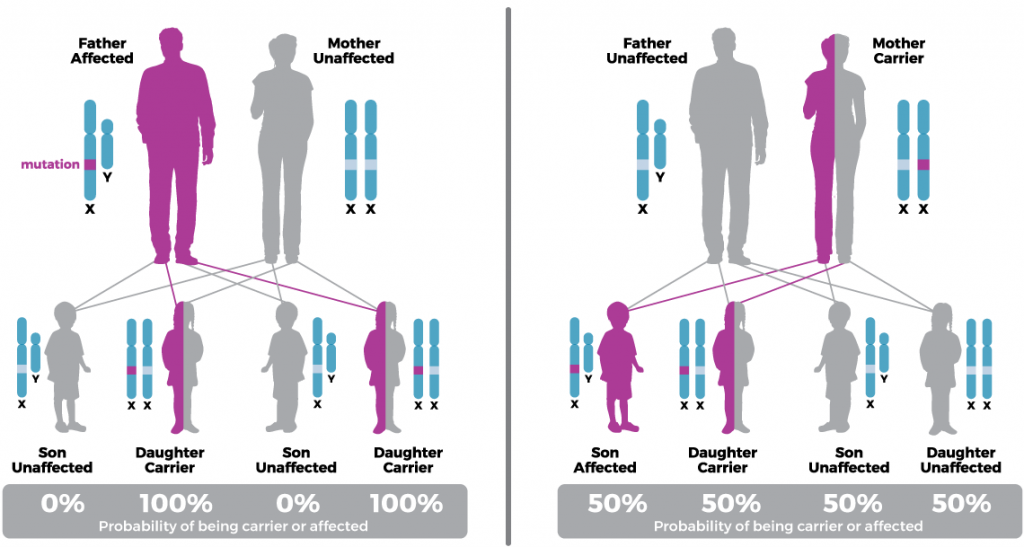
If a father has XLMTM, all of his daughters will become carriers of XLMTM. Daughters/female carriers are frequently asymptomatic, but some present with mild to severe limb weakness, asymmetric muscle loss, respiratory failure, facial weakness, ptosis, and ophthalmoparesis.5,6
If a mother carries a mutation in the MTM1 gene, each of her daughters has a 50% chance of becoming a carrier and each of her sons has a 50% chance of having XLMTM.
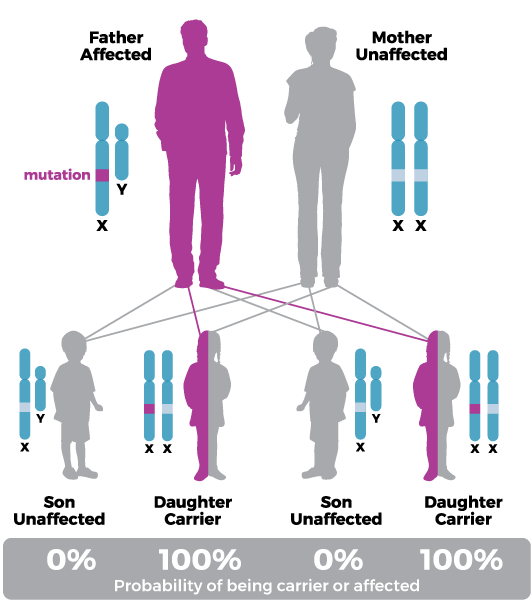
If a father has XLMTM, all of his daughters will become carriers of XLMTM. Daughters/female carriers are frequently asymptomatic, but some present with mild to severe limb weakness, asymmetric muscle loss, respiratory failure, facial weakness, ptosis, and ophthalmoparesis.5,6
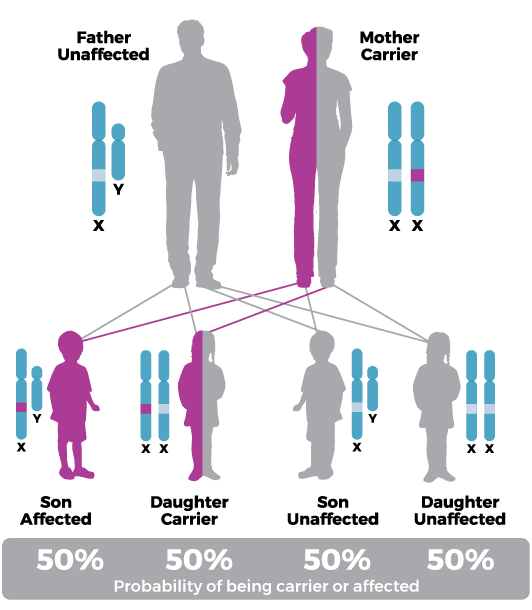
If a mother carries a mutation in the MTM1 gene, each of her daughters has a 50% chance of becoming a carrier and each of her sons has a 50% chance of having XLMTM.

